Ever since OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022, there is so much hype about its insane capabilities and the apprehension that it may ultimately replace Google Search one day. Let’s find out how much of this is true.
Google Search is a Search Engine while ChatGPT is a Chatbot. There is a tendency to think that they can be used interchangeably. However, they work very differently and are meant for different purposes. Let’s compare the different parameters of these two systems and find out how they weigh against each other.
Contents
Source of Data
Google Search returns results from data indexed by its crawlers from the Internet, which means it has access to the latest data and latest happenings. For example, you can ask Google Search to show you the latest news and current affairs.
ChatGPT’s responses are based on OpenAI’s GPT-3.5, an Artificial Intelligence Language model trained on a massive amount of text data from different sources. It has no access to the Internet, and therefore unaware of latest happenings.
Query Model
Google Search is based on a Search Engine model and the querying can take many forms. It is intelligent enough to understand the intent of your search term and return multiple relevant responses. Depending on the query, Google Search may respond with a direct answer, or a detailed answer or just return relevant links, and normally returns the same or very similar results when queried with the same keywords multiple times within a short span of time. Google Search also returns multiple responses in different formats for the same set of keywords. You do not have to be logged in to Google account to use Search.
ChatGPT is an interactive bot designed to provide a human-like conversational experience with detailed answers. It may return different responses to the same prompt, and they’re usually rephrased statements of the same response with different level of information. ChatGPT maintains context in the conversation and further question related to the same topic usually returns more detailed information. ChatGPT returns a single response for any query as it is designed to mimic human conversations. You must be logged in to OpenAI account to use ChatGPT.
Accuracy
Google Search results are generally accurate for pointed questions as they’re fetched from multiple “live” sources and ranked based on importance and accuracy. For general queries, Google Search may at times return irrelevant responses.
ChatGPT may respond with inaccurate and misleading information at times. The responses are as accurate as the data set it is trained on, and suffers from the “garbage in, garbage out” syndrome. ChatGPT is also designed to accept mistakes and provide updated information with subsequent prompts within the same session. This, however, has been proven to be problematic as ChatGPT, at times, blindly accepts the user’s suggestion without challenging it even it the suggestions were deliberately wrong.
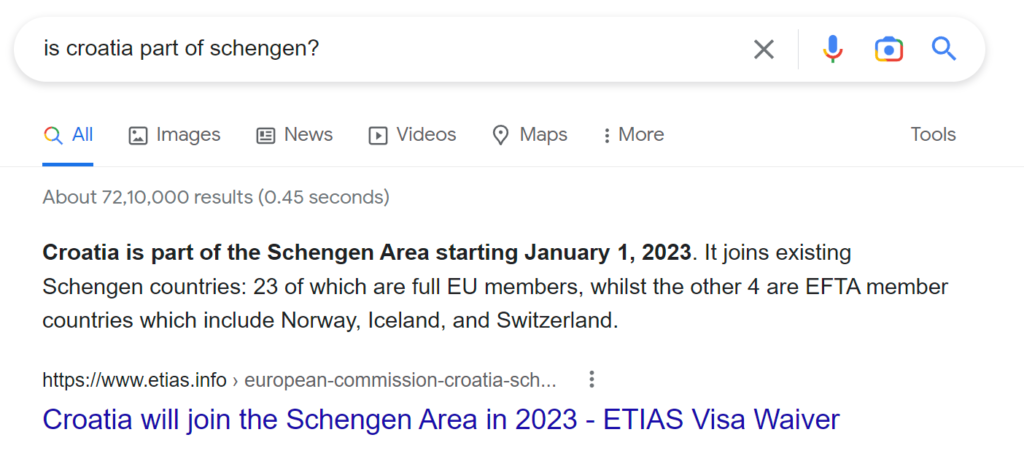
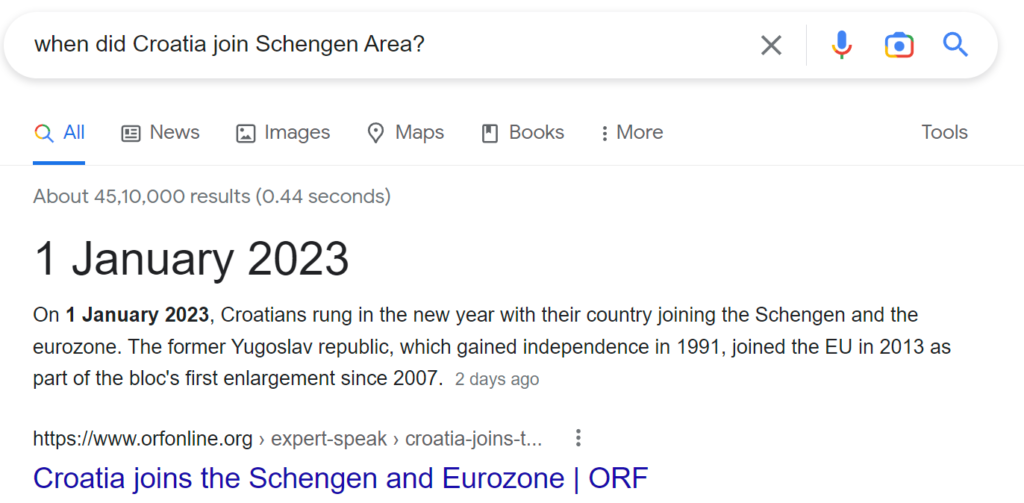
For example, have a look at these questions related to a recent event and see how Google Search returns accurate information and how ChatGPT contradicts itself between two immediate queries.
Google Search
ChatGPT

Privacy
Google Search is governed by its Privacy Policy, and it collects certain information from the users to optimize its search results and provide customized results based on the users’ browsing history and preferences. Privacy is generally a concern when using Search Engines like Google Search since they collect a lot more information than is necessary to provide the results.
ChatGPT is governed by OpenAI’s Privacy Policy. Since you need to login to OpenAI to use ChatGPT, your user information is already captured and linked to the prompts you submit. ChatGPT’s FAQ Page also states that our conversations are captured and used by AI trainers to improve ChatGPT.
Carbon Footprint
The industry standard Carbon footprint for search engines is estimated to be about 0.2 grams of CO2 emission per search. In 2022, Google Search averages about 99,000 searches per second, which translates to roughly 19.8 kg (43.65 lbs) CO2 per second or over 625 million kg (1.38 billion lbs) of CO2 per year.
ChatGPT is not designed for extreme high volume use case like Google Search is. ChatGPT’s current usage is comparatively very low compared to Google Search, and therefore, it is extremely difficult to come up with an accurate Carbon footprint for ChatGPT that truly reflects how it compares to that of Google Search. However, ChatGPT runs on top of GPT-3. Let’s calculate the approximate Carbon footprint of GPT-3 if it has to scale up to handle the traffic equivalent of Google Search.
BLOOM, a large language model similar to GPT-3, was once deployed on a Google Cloud Platform instance with 16 NVIDIA A100 40GB GPUs for 18 days [1]. BLOOM has 176 billion parameters compared to 175 billion parameters of CPT-3, so it makes sense to assume that they have similar infrastructure requirements. This may not be accurate but in the absence of any other estimation model, we are constrained to make such assumptions.
BLOOM emitted 414 kg CO2 to handle 230,768 requests over a period of 18 days. This translates to 178 kg (392 lbs) CO2 per 99,000 requests (each second). Therefore, if ChatGPT were to replace Google Search, it would emit a whopping 5.6 billion kg (12.3 billion lbs) of CO2 per year, which is roughly 9 times than that of Google Search. Note that this number is only an approximation based on available data and depends on a variety of factors. For example, if GPT-3 is hosted on a totally different platform that consumes less electricity and in a region that has lower carbon intensity, the numbers could be drastically low.
| Parameter | Google Search | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 per search | 0.2 grams | 1.79 grams |
| Searches per second | 99,000 | 99,000 |
| CO2 per second | 19.8 kg (43.65 lbs) | 177.6 kg (391.5 lbs) |
| CO2 per year | 625,000,000 kg (1,380,000,000 lbs) | 5,600,000,000 kg (12,300,000,000 lbs) |
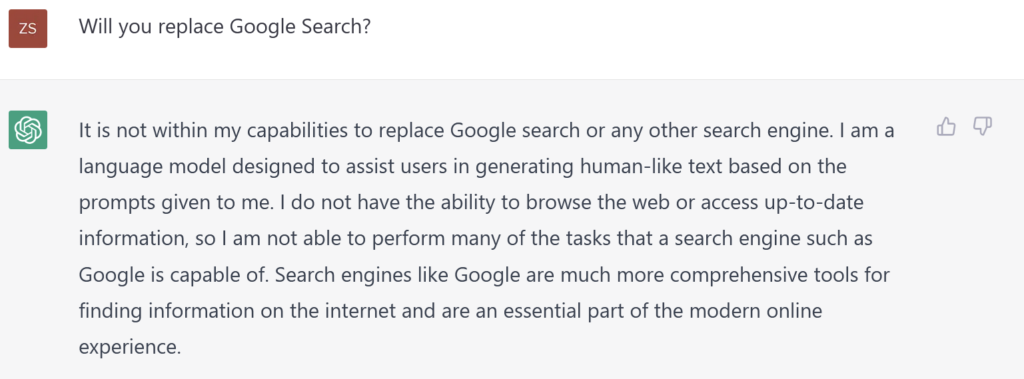
Let ChatGPT Self-evaluate…
Finally, what does ChatGPT think of this topic? Let’s hear from the horse’s mouth…
Conclusion
Using ChatGPT makes sense in certain situations like learning a new language or debugging Python code as it provides an interactive conversational interface similar to human conversations. However, due to scalability limitations, lack of accuracy and extreme carbon footprint requirements to run it at scale at par with Google Search, it still has a long way to go to replace it. At its current avatar, it can only be used in limited situations for very specific uses case for which it is has proven to be a better alternative to Google Search.
References
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.02001.pdf

What an incredibly insightful perspective on the potential of ChatGPT! It’s fascinating to see the advancements in natural language processing and AI-generated responses. While ChatGPT has proven to be remarkably adept at generating human-like conversations, I believe it complements rather than replaces Google search. Both have distinct strengths, and integrating ChatGPT into search engines could enhance user experience by providing more interactive and personalized results. Keep up the great work in exploring cutting-edge technologies! Cheers, GPTOnline.